Hello, Science Adventurers!
Today, we’re going inside one of our body’s most intriguing organs – the pancreas. Tucked snugly into a spot behind your stomach, this unassuming organ is more than meets the eye. From digestion to blood sugar regulation, let’s explore the fascinating world of the pancreas and its role in our body!
Getting to Know the Pancreas
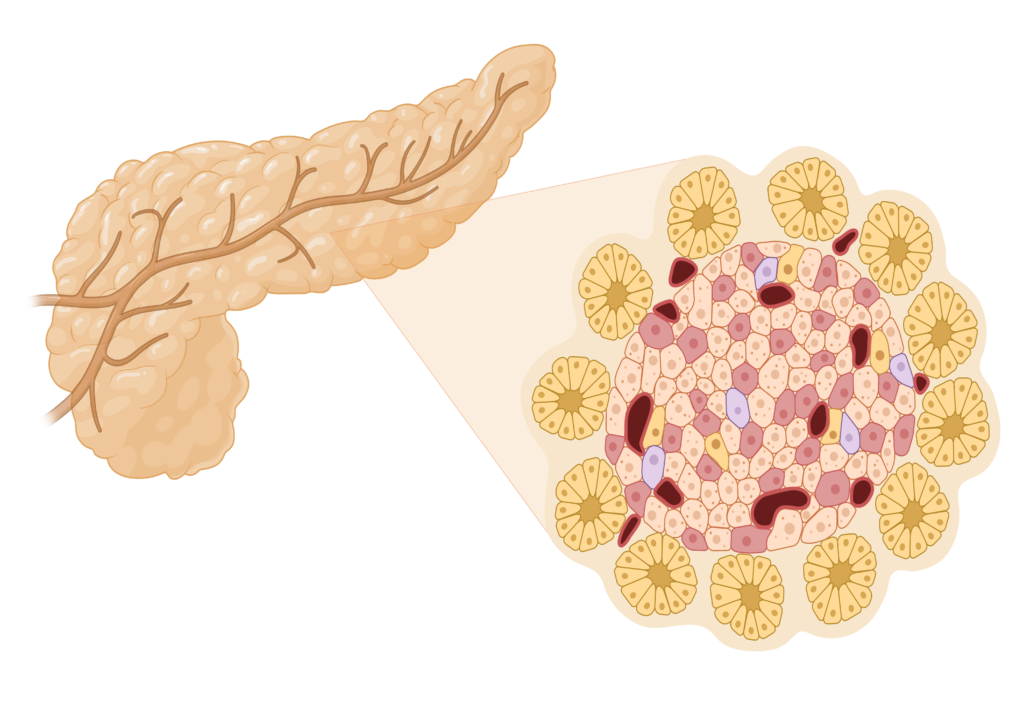
Picture this: a soft, elongated organ between 14-18 cm long and about 2-9 cm wide. It weighs a mere 50-125 grams, roughly the weight of a small apple. This is your pancreas. For ease of understanding, we often divide it into four parts: the head, neck, body, and tail.
A House with Two Rooms: Exocrine and Endocrine
Much like a duplex, our pancreas houses two functional ‘units’ under one roof. The exocrine component is the larger unit, taking up about 98% of the pancreas. Here, acinar cells work tirelessly to produce digestive enzymes that help break down food in the gut.
The smaller ‘unit’, called the endocrine compartment, is a collection of mini-organ clusters known as the islets of Langerhans. Despite being just 2% of the pancreatic volume, these islets are special. They’re responsible for regulating blood sugar in our body. Talk about punching above their weight!
Islets of Langerhans: Mini-organs with a Big Job
Each human pancreas hosts around a million islets, while a mouse’s pancreas houses around 1,000-5,000 islets. Regardless of the species, these tiny organ clusters typically measure between 100 and 200 µm in size. It’s remarkable that something so small plays such a crucial role in our health!
Each islet is a microcosm of cell diversity. They consist of five major cell types, with the most abundant ones being the β-cells (50%) and α-cells (35–40%). These cells are like little factories, manufacturing hormones like insulin (from β-cells) and glucagon (from α-cells) that keep our blood sugar levels in check.
The remaining cells – δ-cells, ε-cells, and pancreatic polypeptide (PP) cells – account for less than 30% of islet cells. They produce other hormones like somatostatin, ghrelin, and pancreatic polypeptide.
Interestingly, the makeup of these islets varies between regions of the pancreas and among different species. For instance, human islets have a higher proportion of α-cells than mouse islets. Even within a species, differences can be observed between males and females!
Beyond the Hormone Factories
In addition to these hormone-producing superstars, islets also host a supporting cast of other cell types. Vascular, immune, neurons and glial cells from the rest of the islet population, play crucial roles in maintaining islet function and health.
Our pancreas is a micro-universe teeming with diverse cells, each playing its part in keeping our body healthy. It’s a testament to the incredible complexity and elegance of our bodies.
So next time you enjoy a balanced meal or a sweet treat, spare a thought for your hardworking pancreas and the millions of islets toiling away to keep your blood sugar levels just right.
Stay curious, stay hungry (for knowledge, of course!), and keep exploring the science that makes us who we are.