Hello, dear devotees of all things scientific!
In today’s blog, we venture into the world of insulin once more, but with a twist. What happens when our bodies start ignoring this tiny yet significant hormone? Welcome to the tale of insulin resistance. Remember, this blog is for education only and doesn’t recommend any health interventions.
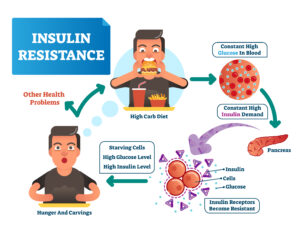
Imagine this: Insulin, our diligent maestro, waving its baton, but the orchestra of cells simply refuses to play along. That’s insulin resistance, in a nutshell. In this scenario, our body doesn’t respond adequately to insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels – a central scene in the narrative of type 2 diabetes (T2DM).
As the rebellion spreads, our pancreatic beta cells overdose, producing even more insulin to pacify the resistant cells. This results in hyperinsulinemia, akin to our conductor yelling at a noisy auditorium, hoping to be heard.
So, who’s more likely to be in this audience of insubordinate cells? It’s been observed that obese individuals, seniors, pregnant women, and occasionally, those hitting puberty, are prone to insulin resistance (Buchanan et al., 1990; Sonagra et al., 2014).
The plot thickens with the role of abdominal fat, especially in obese individuals. These fats resist insulin’s call for order, increasing the level of non-esterified fatty acids (NEFA) in the blood. Studies have linked elevated NEFA levels to insulin resistance and impaired glucose tolerance (Roden et al., 1997; Zeirath et al., 1998).
NEFA, like moles infiltrating a fortress, enter cells and create havoc in the form of various metabolites. These troublemakers activate a series of events leading to the inactivation of insulin’s signalling soldiers, IRS1, and IRS-2, hindering glucose’s entry into the cells.
Alternatively, these rebellious NEFAs can cause an imbalance in the cells’ energy state, leading to the inactivation of crucial enzymes involved in glucose breakdown. This brings the cellular glucose uptake process to a grinding halt (Randle et al., 1963; Shulman, 2000).
Further complicating matters, certain inflammatory molecules, such as TNF-α and IL-6, released from fat tissues, act as negative influencers, dampening insulin’s influence on cells (Kahn et al., 2006; Tangvarasittichai et al., 2016).
In the saga of our body’s metabolic balance, insulin resistance appears as an intriguing plot twist, disrupting the harmonious relationship between insulin and our cells. As we continue our journey of understanding, let’s remain captivated but cautious, embracing knowledge but always seeking professional medical advice when needed.
Stay tuned for more such intriguing tales from the microscopic universe within us!
P.S. Always remember that the knowledge here is meant to fascinate and educate, not to be mistaken for medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for health-related concerns.